A) both the changes in information technology and unemployment insurance
B) only the changes in information technology
C) only the changes in unemployment insurance
D) neither the changes in information technology nor the changes in unemployment insurance
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-1 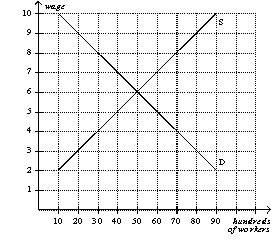 -Refer to Figure 15-1.If the government imposes a minimum wage of $4,then how many workers will be employed?
-Refer to Figure 15-1.If the government imposes a minimum wage of $4,then how many workers will be employed?
A) 3000
B) 4000
C) 5000
D) 7000
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
People who report being not in the labor force but who,in fact,want to work but have given up trying to find a job after an unsuccessful search cause the reported unemployment rate to be lower than it would otherwise be.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the minimum wage were currently above the equilibrium wage,then a decrease in the minimum wage that kept it above the equilibrium wage would
A) increase the surplus of labor.
B) reduce the surplus of labor.
C) increase the shortage of labor.
D) reduce the shortage of labor,
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics produces data on unemployment and other aspects of the labor market from a regular survey of about
A) 600 households.
B) 6,000 households.
C) 60,000 households.
D) 6,000,000 households.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Not all unemployment ends with the job seeker finding a job.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the U.S. ,it is illegal for employers to interfere when workers try to organize unions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the U.S. ,the National Labor Relations Board is the government agency that enforces workers' right to unionize.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An American worker who becomes unemployed typically receives 100% of her former salary during the first six months she is unemployed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
More than three-fourths of the unemployed are recent entrants into the labor force.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions contribute to
A) frictional unemployment but not the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment but not frictional unemployment.
C) both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
D) neither frictional unemployment nor the natural rate of unemployment.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Meredith recently graduated from college but has not yet started working.To be counted as unemployed she
A) does not have to have looked for work.
B) must have looked for work no more than a week ago.
C) must have looked for work no more than 4 weeks ago.
D) must have looked for work no more than 12 weeks ago.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following includes everyone in the adult population that the Bureau of Labor Statistics counts as unemployed?
A) anyone who is not employed
B) anyone who is not employed,is available for work,and has looked for work in the past 4 weeks
C) anyone who is not employed,is available for work,has looked for work in the past 4 weeks,and anyone who is waiting to be recalled from a job from which they have been laid off
D) anyone who is not employed,is available for work,has looked for work in the past 4 weeks,anyone who is waiting to be recalled from a job from which they have been laid off,and anyone who is employed part time and has searched for full time employment in the past 4 weeks
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Providing training for unemployed individuals is primarily intended to reduce
A) frictional unemployment.
B) seasonal unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) cyclical unemployment.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Scenario 28-1.What is the total labor force?
A) 25 million
B) 28 million
C) 29 million
D) 30 million
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adam is looking for a job in marketing.He has had some offers and his prospects are promising but he's not yet accepted a job.Amanda lost her job working for Mercury Bicycles because many customers decided they prefer bicycles manufactured by Ultimate Bicycles instead.Who is frictionally unemployed?
A) Adam but not Amanda
B) Amanda but not Adam
C) Adam and Amanda
D) neither Amanda nor Adam
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is only among the least skilled and least experienced members of the labor force that minimum-wage laws cause unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) Frictional unemployment is inevitable in a dynamic economy.
B) Although the unemployment created by sectoral shifts is unfortunate,in the long run such changes lead to higher productivity and higher living standards.
C) At least 10 percent of U.S.manufacturing jobs are destroyed every year.
D) More than 13 percent of U.S.workers leave their jobs in a typical month.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider two people who are currently out of work.Tim is not looking for work because there have been many job cuts where he lives and he doesn't think it likely that he will find work.Bev is not currently looking for work,but she would like a job and she has looked for work in the past.The Bureau of Labor Statistics considers
A) both Tim and Bev to be marginally attached workers.
B) neither Tim nor Bev to be marginally attached workers.
C) only Tim to be a marginally attached worker.
D) only Bev to be a marginally attached worker.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) An organized withdrawal of labor from a firm by a union is called a strike.
B) The power of a union comes from its ability to strike if the union and the firm do not agree on the terms of employment.
C) Economists who study the effects of unions typically find that union workers earn about 25 to 35 percent more than similar workers who do not belong to unions.
D) Workers in unions reap the benefit of collective bargaining,while workers not in unions bear some of the cost.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 610
Related Exams