A) You continue studying for your economics exam until you believe you'll get a score that's good enough.
B) You spend time looking over the lettuce at the grocery store in order to make sure you get the best head of lettuce.
C) You clean your room to the point where you think it's clean enough that further time can be used for more productive purposes.
D) You carefully plan your day in order to get "the most out of life."
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rick goes to work 8 hours per day, but while he is at work he spends most of his time visiting internet sites monitoring his fantasy football teams. This is an example of
A) the Condorcet Paradox.
B) signaling.
C) moral hazard.
D) screening.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The temptation of imperfectly-monitored workers to shirk their responsibilities is
A) an example of the moral hazard problem.
B) an example of the adverse selection problem.
C) an example of screening.
D) an example of signaling.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Smoking cessation tools (e.g., nicotine gum) provide evidence that people behave in a time inconsistent manner.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In American politics, we often observe that during a campaign, the Democratic and Republican positions on many issues are similar, which illustrates
A) Arrow's impossibility theorem.
B) the Condorcet paradox.
C) a Borda count.
D) the median voter theorem.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Latin term caveat emptor, meaning "let the buyer beware," brings to mind the problem of
A) hidden actions.
B) adverse selection.
C) principals and agents.
D) moral hazard.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A college professor hires a student to babysit her children and pays the student an efficiency-wage. Which of the following is correct about the wage the student earns?
A) The wage is higher than the wage the student could earn working a similar job elsewhere.
B) The wage is the same as the wage the student could earn working a similar job elsewhere.
C) The wage is lower than the wage the student could earn working a similar job elsewhere.
D) The wage is likely to result in the student shirking responsibilities.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The median-voter theorem explains why
A) politicians take extreme stands on issues.
B) voters are attracted to political outsiders.
C) two opposing politicians tend to take opposite sides of each issues.
D) politicians tend to take middle-of-the-road positions.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his 1951 book, Social Choice and Individual Values, Kenneth Arrow used the term "unanimity" to mean
A) A beats B only if everyone prefers A to B.
B) if everyone prefers A to B, then A beats B.
C) if A beats B and B beats C, then A must best C.
D) everyone who is eligible to vote must vote; otherwise, the outcome is invalid.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that residents of a town are asked to vote on the best day to improve the safety of an intersection. The three choices are: a stoplight, a 4-way stop, and a 2-way stop. The mayor asks the residents to assign 3 points to their first choice, 2 points to their second choice, and 1 point to their last choice. The intersection will be controlled by the method that receives the most points. This voting scheme is called
A) Arrow's impossibility theorem.
B) the Condorcet paradox.
C) a Borda count.
D) the median voter theorem.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-6  -Refer to Table 22-6. The table shows the preferences of 100 voters over three possible outcomes: A, B, and C. Which of the following statements is true?
-Refer to Table 22-6. The table shows the preferences of 100 voters over three possible outcomes: A, B, and C. Which of the following statements is true?
A) In pairwise majority voting, B is preferred to A, A is preferred to C, and B is preferred to C.
B) In pairwise majority voting, C is preferred to B, B is preferred to A, and C is preferred to A.
C) In pairwise majority voting, B is preferred to A, A is preferred to C, and C is preferred to B.
D) In pairwise majority voting, A is preferred to C, C is preferred to B, and A is preferred to B.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-14
Amy, Beth, and Connie are on a hiring committee. They have interviewed 3 candidates identified by their last names and are going to vote on which one is hired.  '
-Refer to Table 22-14. Adams calls and says she's accepted another position. In which case does Campbell win against Brown?
'
-Refer to Table 22-14. Adams calls and says she's accepted another position. In which case does Campbell win against Brown?
A) both a pairwise vote and a Borda Count vote
B) a pairwise vote, but not a Borda Count vote
C) a Borda Count vote, but not a pairwise vote
D) neither a Borda Count vote, nor a pairwise vote
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When homeowners sell a house, part of the paperwork they complete is a statement of disclosure on which the homeowners are supposed to reveal everything that they know is wrong with the house. The purpose of the statement of disclosure is to try to solve the
A) principal-agent problem.
B) moral-hazard problem.
C) adverse-selection problem.
D) signaling problem.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most economic models
A) incorporate the assumption of rational behavior on the part of economic actors.
B) incorporate the notion that people are usually reluctant to change their minds.
C) are meant to precisely duplicate reality.
D) assume that people often make sub-optimal choices.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a corporation decides to include its own corporate stock as part of the compensation for its employees, it is trying to solve the
A) adverse selection problem.
B) principal-agent problem.
C) lemons problem.
D) signaling problem.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-2
Three longtime friends-Allen, Brian, and Cody-are deciding how they will spend their Sunday afternoon. They all agree that they should do one of three things: go to a movie, play golf, or go to a baseball game. They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine how to spend their afternoon, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote. The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below. 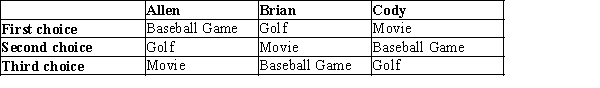 -Refer to Table 22-2. If (1) the first vote pits "baseball game" against "movie," and (2) the second vote pits "golf" against the winner of the first vote, then the outcome is as follows:
-Refer to Table 22-2. If (1) the first vote pits "baseball game" against "movie," and (2) the second vote pits "golf" against the winner of the first vote, then the outcome is as follows:
A) "Baseball game" wins the first vote and "baseball game" wins the second vote, so they go to a baseball game.
B) "Baseball game" wins the first vote and "golf" wins the second vote, so they go to the golf.
C) "Movie" wins the first vote and "movie" wins the second vote, so they go to a movie.
D) "Movie" wins the first vote and "golf" wins the second vote, so they play golf.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The classic example of adverse selection is the
A) market for used cars.
B) market for new cars.
C) relationship between shareholders and managers.
D) relationship between a coach and an athlete.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-1
Three friends -- Linda, Stephanie, and Jamie -- are deciding where to go together for vacation. They all agree that they should go to one of three places: France, Greece, or Italy. They also agree that they will have two pairwise votes to determine where to go on vacation, with the majority determining the outcome on each vote. The first, second, and third choices for each person are as indicated in the table below. 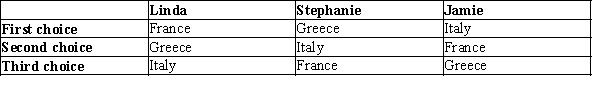 -Refer to Table 22-1. If the friends change their minds and decide to choose a vacation destination using a Borda count, then
-Refer to Table 22-1. If the friends change their minds and decide to choose a vacation destination using a Borda count, then
A) the friends will go to France.
B) the friends will go to Greece.
C) the friends will go to Italy.
D) A Borda count will not result in a single winner in this case.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A community has five voters who are interested in only one issue: the government's spending on local parks. If Andre would like the government to spend $12,000 on parks, Brandon prefers $7,000, Charlene prefers $4,000, Dennis prefers $2,000, and Ernie prefers $0, how much spending would a politician seeking to win the election select when running against one opponent?
A) $2,000
B) $4,000
C) $7,000
D) $12,000
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People with hidden health problems are more likely to buy health insurance than are other people. This is an example of
A) moral hazard and makes the cost of health insurance higher than otherwise.
B) moral hazard and makes the cost of health insurance lower than otherwise.
C) adverse selection and makes the cost of health insurance higher than otherwise.
D) adverse selection and makes the cost of health insurance lower than otherwise.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 461
Related Exams