A) Non-U.S.persons may be subject to U.S.withholding tax on U.S.-source investment income.
B) Non-U.S.individuals may be subject to U.S.income tax but non-U.S.corporations are never subject to U.S.income tax.
C) Non-U.S.persons are subject to U.S.income or withholding tax only if engaged in a U.S.trade or business.
D) Non-U.S.persons must be physically present in the United States before any U.S.-source income is subject to U.S.income or withholding tax.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Without the foreign tax credit, double taxation would result when:
A) The United States taxes the U.S.-source income of a U.S.resident.
B) A foreign country taxes the foreign-source income of a nonresident alien.
C) The United States and a foreign country both tax the foreign-source income of a U.S.resident.
D) Terms of a tax treaty assign income taxing rights to the United States.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a principle used in applying the income-sourcing rules under U.S.tax law?
A) The rules should be acceptable to both countries.
B) The rules should favor the U.S.Treasury.
C) The rules should favor the treasury of the non-U.S.country.
D) The rules should apply to income items only; deductions need not be sourced in this way.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Kipp, a U.S.shareholder under the CFC provisions, owns 40% of a CFC.If the CFC's Subpart F income for the taxable year is $200,000, Kipp is taxed on receipt of a constructive dividend of $80,000.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The United States has in force income tax treaties with about 70 countries.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Subpart F income includes portfolio income such as dividends and interest.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding a non-U.S.person's U.S.tax consequences is true?
A) Non-U.S.persons may be subject to withholding tax on U.S.-source investment income even if not engaged in a U.S.trade or business.
B) Non-U.S.persons are subject to U.S.income or withholding tax only if they are engaged in a U.S.trade or business.
C) Non-U.S.persons are not taxed on gains from U.S.real property as long as such property is not used in a U.S.trade or business.
D) Once a non-U.S.person is engaged in a U.S.trade or business, the non-U.S.person's worldwide income is subject to U.S.taxation.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A unitary group of entities files a combined return that includes all of the affiliates' income and apportionment data.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A U.S.taxpayer may take a current FTC equal to the greater of the FTC limit or the actual foreign taxes (direct or indirect) paid or accrued.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
U.S.income tax treaties can be described as:
A) Napoleonic.
B) Spoke-and-Wheel.
C) Balanced.
D) Bilateral.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Hendricks Corporation, a domestic corporation, owns 40 percent of Shane Corporation and 55 percent of Ferrell Corporation, both foreign corporations.Ferrell owns the other 60 percent of Shane Corporation.Both Shane and Ferrell are CFCs.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
All of the U.S.states have adopted a tax based on the net taxable income of corporations.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Unused foreign tax credits are carried back two years and then forward 20 years.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A state can levy an income tax on a business only if the business was incorporated in the state.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Property taxes generally are collected by local taxing jurisdictions, not the state or Federal governments.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adams Corporation owns and operates two manufacturing facilities, one in State X and the other in State Y.Due to a temporary decline in the corporation's sales, Adams has rented 20% of its Y facility to an unaffiliated corporation.Adams generated $1,000,000 net rental income and $5,000,000 income from manufacturing. Adams is incorporated in Y.For X and Y purposes, rental income is classified as allocable nonbusiness income.By applying the statutes of each state, Adams determined that its apportionment factors are 0.65 for X and 0.35 for Y. Adams's income attributed to X is:
A) $0.
B) $3,250,000.
C) $3,900,000.
D) $5,000,000.
E) $6,000,000.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In working with the foreign tax credit, a U.S.corporation may be able to alleviate the problem of excess foreign taxes by:
A) Deducting the excess foreign taxes that do not qualify for the credit.
B) Repatriating more foreign income to the United States in the year there is an excess limitation.
C) Generating "same basket" foreign-source income that is subject to a tax rate higher than the U.S.tax rate.
D) Generating "same basket" foreign-source income that is subject to a tax rate lower than the U.S.tax rate.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Under P.L.86-272, the taxpayer is exempt from state taxes on income resulting from the mere solicitation of orders for the sale of stocks and bonds.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In determining state taxable income, all of the following are adjustments to Federal income except:
A) Federal net operating loss.
B) State income tax expense.
C) Fringe benefits paid to officers and executives.
D) Dividends received from other U.S.corporations.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marquardt Corporation realized $900,000 taxable income from the sales of its products in States X and Z. Marquardt's activities establish nexus for income tax purposes in both states.Marquardt's sales, payroll, and property among the states include the following: 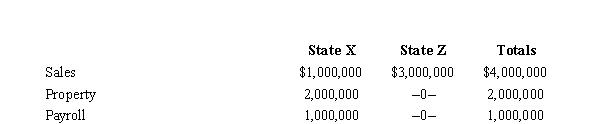 Z utilizes an equally weighted three-factor apportionment formula.Marquardt is incorporated in X.How much of Marquardt's taxable income is apportioned to Z?
Z utilizes an equally weighted three-factor apportionment formula.Marquardt is incorporated in X.How much of Marquardt's taxable income is apportioned to Z?
A) $0
B) $225,000
C) $675,000
D) $3,000,000
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 91
Related Exams