A) is unaffected.
B) decreases.
C) increases.
D) There is not enough information given in answer the question.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The demand curve facing a competitive firm is horizontal, as is the demand curve facing a monopolist.
B) The demand curve facing a competitive firm is downward sloping, whereas the demand curve facing a monopolist is horizontal.
C) The demand curve facing a competitive firm is horizontal, whereas the demand curve facing a monopolist is downward sloping.
D) The demand curve facing a competitive firm is downward sloping, as is the demand curve facing a monopolist.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following may eliminate some or all of the inefficiency that results from monopoly pricing?
A) The government can regulate the monopoly.
B) The monopoly can be prohibited from price discriminating.
C) The monopoly can be forced to operate at a point where its marginal revenue is equal to its marginal cost.
D) None of the above would eliminate any inefficiency associated with a monopoly.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The profit that a monopolist earns represents a loss to society that is measured through deadweight loss.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopoly creates a deadweight loss to society because it produces less output than the socially efficient level.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
By selling hardcover books to die-hard fans and paperback books to less enthusiastic readers,the publisher is able to price discriminate and raise its profits.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-1
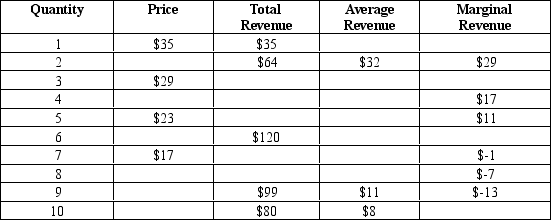 -Refer to Table 15-1.Assume this monopolist's marginal cost is constant at $12.What quantity of output (Q) will it produce and what price (P) will it charge?
-Refer to Table 15-1.Assume this monopolist's marginal cost is constant at $12.What quantity of output (Q) will it produce and what price (P) will it charge?
A) Q = 4, P = $29
B) Q = 4, P = $26
C) Q = 5, P = $23
D) Q = 7, P = $17
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a firm has a natural monopoly,the firm's
A) marginal cost always exceeds its average total cost.
B) total cost curve is horizontal.
C) average total cost curve is downward sloping.
D) marginal cost curve must lie above the firm's average total cost curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The benefits that accrue to a monopoly's owners are equal to the costs that are incurred by consumers of that firm's product.
B) The deadweight loss that arises in monopoly stems from the fact that the profit-maximizing monopoly firm produces a quantity of output that exceeds the socially-efficient quantity.
C) The deadweight loss caused by monopoly is similar to the deadweight loss caused by a tax on a product.
D) The primary social problem caused by monopoly is monopoly profit.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-8
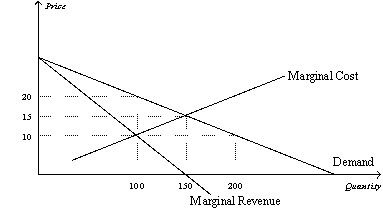 -Refer to Figure 15-8.To maximize total surplus,a benevolent social planner would choose which of the following outcomes?
-Refer to Figure 15-8.To maximize total surplus,a benevolent social planner would choose which of the following outcomes?
A) 100 units of output and a price of $10 per unit
B) 150 units of output and a price of $10 per unit
C) 150 units of output and a price of $15 per unit
D) 200 units of output and a price of $10 per unit
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopolist's supply curve is vertical.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a competitive market,a firm's supply curve dictates the amount it will supply.In a monopoly market the
A) same is true.
B) supply curve conceptually makes sense, but in practice is never used.
C) supply curve will have limited predictive capacity.
D) decision about how much to supply is impossible to separate from the demand curve it faces.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopoly firm is a price
A) taker and has no supply curve.
B) maker and has no supply curve
C) taker and has an upward-sloping supply curve.
D) maker and has an upward-sloping supply curve.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Declining average total cost with increased production is one of the defining characteristics of a natural monopoly.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-2
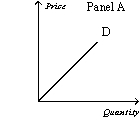
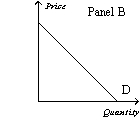
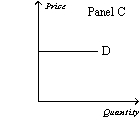
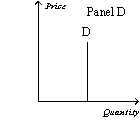 -Refer to Figure 15-2.Which of the following statements is correct?
-Refer to Figure 15-2.Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Panel C represents the typical demand curve for a perfectly competitive industry.
B) Panel B represents the typical demand curve for a monopoly.
C) Panel B represents the typical demand curve for a perfectly competitive firm.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The assessment by George Stigler concerning the tradeoffs between "market failure" and "political failure" in the American economy provides support for which of the following solutions to the problems of monopolies?
A) public ownership of monopolies
B) government regulation of monopolies
C) government incentives to promote competition in monopolized industries
D) doing nothing at all
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a constant marginal cost of $10,produces an output level of 100 units,and charges a price of $50.The socially efficient level of output is 200 units.Assume that the demand curve and marginal revenue curve are the typical downward-sloping straight lines.The monopoly deadweight loss equals $2,000.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a constant marginal cost of $10,produces an output level of 100 units,and charges a price of $50.The socially efficient level of output is 200 units.Assume that the demand curve and marginal revenue curve are the typical downward-sloping straight lines.The monopoly deadweight loss equals $4,000.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) Antitrust laws may prevent mergers that would actually raise social welfare.
B) Public ownership is the most common public policy toward monopolies in the United States.
C) Regulation is a common strategy for a natural monopoly.
D) Sometimes the best public policy toward a monopoly may be to do nothing.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 15-2
Tanya has the following demand curve for selling taffy. Assume that Tanya has a marginal cost of $3 per unit.
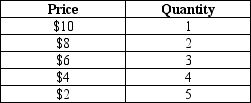 -Refer to Table 15-2.What is Tanya's profit-maximizing price?
-Refer to Table 15-2.What is Tanya's profit-maximizing price?
A) $2
B) $4
C) $6
D) $8
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 526
Related Exams