A) monopoly
B) perfect competition
C) monopolistic competition
D) oligopoly
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which market structure would likely have the highest concentration ratio?
A) Monopoly
B) Oligopoly
C) Monopolistic competition
D) Perfect competition
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The product-variety externality arises in monopolistically competitive markets because
A) firms produce with excess capacity.
B) firms try to differentiate their products.
C) firms would like to produce homogeneous products, but the large number of firms prohibits it.
D) entry and exit is restricted.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The government may not be able to improve the inefficiencies of a monopolistically competitive market.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-2
This figure depicts a situation in a monopolistically competitive market.
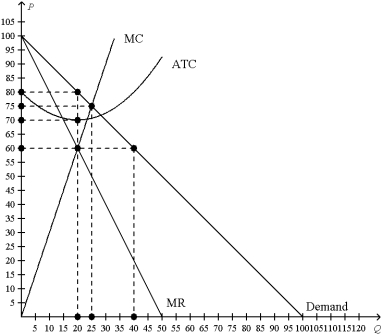 -Refer to Figure 16-2.What is the profit-maximizing price,quantity,and resulting profit?
-Refer to Figure 16-2.What is the profit-maximizing price,quantity,and resulting profit?
A) P=$60, Q=20 units, profit=$200
B) P=$80, Q=20 units, profit=$200
C) P=$75, Q=25 units, profit=$100
D) P=$60, Q=40 units, profit=$0
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because a monopolistically competitive firm has some market power,in the long-run the price of its product exceeds its
A) average revenue.
B) average total cost.
C) marginal cost.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a long-run equilibrium,a firm in a monopolistically competitive market operates
A) where marginal revenue is zero.
B) where marginal revenue is negative.
C) on the rising portion of its average total cost curve.
D) on the declining portion of its average total cost curve.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some firms have an incentive to advertise because they sell a
A) homogeneous product and charge a price equal to marginal cost.
B) homogeneous product and charge a price above marginal cost.
C) differentiated product and charge a price equal to marginal cost.
D) differentiated product and charge a price above marginal cost.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the long run,monopolistically competitive firms produce where demand equals marginal cost.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 16-4
This table shows the demand schedule, marginal cost, and average total cost for a monopolistically competitive firm.
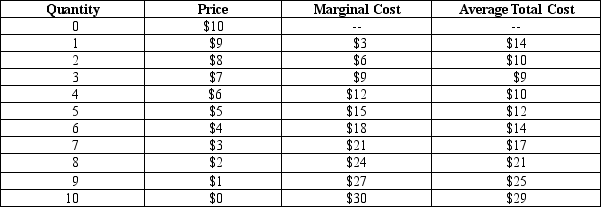 -Refer to Table 16-4.At the profit maximizing level of output,what is this firm's total cost?
-Refer to Table 16-4.At the profit maximizing level of output,what is this firm's total cost?
A) $0
B) $14
C) $20
D) $27
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The market for novels is
A) perfectly competitive.
B) a monopoly.
C) monopolistically competitive.
D) an oligopoly.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a monopolistically competitive market,
A) the entry of new firms creates externalities.
B) the absence of restrictions on entry by new firms ensures that there will be no deadweight loss.
C) there are always too many firms in the market relative to the socially-optimal number of firms.
D) firms cannot earn positive economic profits in the short run.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As new firms enter a monopolistically competitive market,profits of existing firms
A) rise, and product diversity in the market increases.
B) rise, and product diversity in the market decreases.
C) decline, and product diversity in the market increases.
D) decline, and product diversity in the market decreases.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-8
The figure is drawn for a monopolistically-competitive firm.
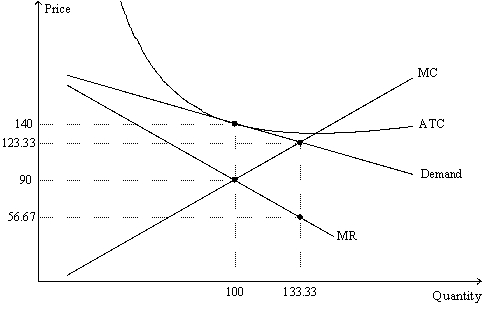 -Refer to Figure 16-8.For this firm,the long-run equilibrium quantity of output is
-Refer to Figure 16-8.For this firm,the long-run equilibrium quantity of output is
A) 100 and the long-run equilibrium price is $90.
B) 100 and the long-run equilibrium price is $140.
C) 133.33 and the long-run equilibrium price is $56.67.
D) 133.33 and the long-run equilibrium price is $123.33.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In monopolistically competitive markets,economic losses
A) suggest that some existing firms will exit the market.
B) suggest that new firms will enter the market.
C) are minimized through government-imposed barriers to entry.
D) are never possible.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Both monopolistic competition and oligopoly are market structures
A) that fail to achieve the total surplus achieved by perfect competition.
B) that feature only a few firms in each market.
C) to which the concept of Nash equilibrium is frequently applied by economists.
D) in which firms earn zero economic profit in the long run.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A business-stealing externality is
A) an externality that is likely to be punished under antitrust laws.
B) the negative externality that occurs when one firm attempts to duplicate exactly the product of a different firm.
C) an externality that is considered to be an explicit cost of business in monopolistically competitive markets.
D) the negative externality associated with entry of new firms in a monopolistically competitive market.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The government of Italy will not allow any Hard Rock Cafe restaurants to open in Italy.Defenders of the efficiency of brand-name markets would argue that this has hindered restaurant market efficiency in Italy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Entry and exit drive each firm in a monopolistically competitive market to a point of tangency between its
A) marginal revenue curve and its total cost curve.
B) marginal revenue curve and its average total cost curve.
C) demand curve and its total cost curve.
D) demand curve and its average total cost curve.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) Novels are likely to be produced in a monopolistically competitive industry.
B) Cable television is likely to be produced in a monopoly industry.
C) Milk is likely to be produced in a monopolistically competitive industry.
D) Cigarettes are likely to be produced in an oligopoly industry.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 241 - 260 of 497
Related Exams