B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If net exports fall $40 billion and the MPC is 8/11 and there is a multiplier effect, but no crowding out and no investment accelerator, then
A) aggregate demand falls by 3 x $40 billion.
B) aggregate demand falls by 11/3 x $40 billion.
C) aggregate demand falls by 11/8 x $40 billion.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-6. On the left-hand graph, MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph, AD represents aggregate demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs. 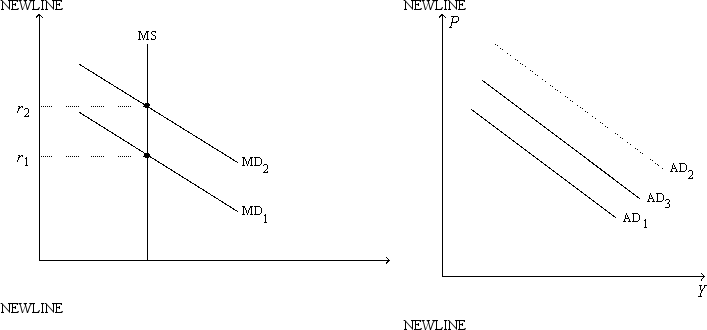 -Refer to Figure 21-6. Suppose the multiplier is 5 and the government increases its purchases by $10 billion. Also, suppose the AD curve would shift from AD1 to AD2 if there were no crowding out; the AD curve actually shifts from AD1 to AD3 with crowding out. Also, suppose the horizontal distance between the curves AD1 and AD3 is $20 billion. The extent of crowding out, for any particular level of the price level, is
-Refer to Figure 21-6. Suppose the multiplier is 5 and the government increases its purchases by $10 billion. Also, suppose the AD curve would shift from AD1 to AD2 if there were no crowding out; the AD curve actually shifts from AD1 to AD3 with crowding out. Also, suppose the horizontal distance between the curves AD1 and AD3 is $20 billion. The extent of crowding out, for any particular level of the price level, is
A) the horizontal distance between the curves MD1 and MD2.
B) $40 billion.
C) $30 billion.
D) $20 billion.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the MPC is 0.60; there is no investment accelerator; and there are no crowding-out effects. If government expenditures increase by $25 billion, then aggregate demand
A) shifts rightward by $62.5 billion.
B) shifts rightward by $50.0 billion.
C) shifts rightward by $32.5 billion.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Some economists, called supply-siders, argue that changes in the money supply exert a strong influence on aggregate supply.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in government spending initially and primarily shifts
A) aggregate demand to the right.
B) aggregate demand to the left.
C) aggregate supply to the right.
D) neither aggregate demand nor aggregate supply in either direction.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of liquidity preference illustrates the principle that
A) monetary policy can be described either in terms of the money supply or in terms of the interest rate.
B) monetary policy can be described either in terms of the exchange rate or the interest rate.
C) monetary policy must be described in terms of the money supply.
D) monetary policy must be described in terms of the interest rate.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When there is an increase in government expenditures, which of the following raises investment spending?
A) the investment accelerator and crowding out
B) the investment accelerator but not crowding out
C) crowding out but not the investment accelerator
D) neither the investment accelerator or crowding out
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the effects listed below increases the quantity of goods and services demanded when the price level falls and decreases the quantity of goods and services demanded when the price level rises?
A) the wealth effect
B) the interest-rate effect
C) the exchange-rate effect
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal, in the short run a higher price level leads households to
A) increase consumption and firms to buy more capital goods.
B) increase consumption and firms to buy fewer capital goods.
C) decrease consumption and firms to buy more capital goods.
D) decrease consumption and firms to buy fewer capital goods.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Fed is concerned about stock market booms because the booms
A) increase consumption spending.
B) increase investment spending.
C) increase both consumption and investment spending.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A policy that results in slow and steady growth of the money supply is an example of
A) an "easy" monetary policy.
B) a "passive" monetary policy.
C) a "practical" monetary policy.
D) an "active" monetary policy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Initially, the economy is in long-run equilibrium. The aggregate demand curve then shifts $80 billion to the left. The government wants to change spending to offset this decrease in demand. The MPC is 0.75. Suppose the effect on aggregate demand of a tax change is 3/4 as strong as the effect of a change in government expenditure. There is no crowding out and no accelerator effect. What should the government do if it wants to offset the decrease in real GDP?
A) Raise both taxes and expenditures by $80 billion dollars.
B) Raise both taxes and expenditures by $10 billion dollars.
C) Reduce both taxes and expenditures by $80 billion dollars.
D) Reduce both taxes and expenditures by $10 billion dollars.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following effects results from the change in the interest rate created by an increase in government spending?
A) the investment accelerator and crowding out
B) the investment accelerator but not crowding out
C) crowding out but not the investment accelerator
D) neither crowding out nor the investment accelerator
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In principle, the government could increase the money supply or increase government expenditures to try to offset the effects of a wave of pessimism about the future of the economy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, automatic stabilizers tend to
A) raise expenditures during expansions and recessions.
B) lower expenditures during expansions and recessions.
C) raise expenditures during recessions and lower expenditures during expansions.
D) raise expenditures during expansions and lower expenditures during recessions.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The multiplier effect
A) and the crowding-out effect both amplify the effects of an increase in government expenditures.
B) and the crowding-out effect both diminish the effects of an increase in government expenditures.
C) diminishes the effects of an increase in government expenditures, while the crowding-out effect amplifies the effects.
D) amplifies the effects of an increase in government expenditures, while the crowding-out effect diminishes the effects.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following shifts aggregate demand to the right?
A) The price level rises.
B) The price level falls.
C) The Fed purchases government bonds on the open market.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tax cuts
A) and increases in government expenditures shift aggregate demand right.
B) and increases in government expenditures shift aggregate demand left.
C) shift aggregate demand right while increases in government expenditures shift aggregate demand left.
D) shift aggregate demand left while increases in government expenditures shift aggregate demand right.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following policies would Keynes's followers support when an increase in business optimism shifts the aggregate demand curve away from long-run equilibrium?
A) decrease taxes
B) increase government expenditures
C) increase the money supply
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 281 - 300 of 416
Related Exams