B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Government expenditures on capital goods such as roads could increase aggregate supply. Such effects on aggregate supply are likely to matter more in the short run than in the long run.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The wealth effect helps explain the slope of the aggregate-demand curve. This effect is
A) relatively important in the United States because expenditures on consumer durables is very responsive to changes in wealth.
B) relatively important in the United States because consumption spending is a large part of GDP.
C) relatively unimportant in the United States because money holdings are a small part of consumer wealth.
D) relatively unimportant because it takes a large change in wealth to cause a significant change in interest rates.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to a 2009 article in The Economist, the multiplier effect and crowding-out effect would exactly offset each other when the economy is
A) operating at full capacity.
B) in recession.
C) experiencing zero inflation.
D) experiencing high rates of inflation.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, use the diagram below:
Figure 21-7. 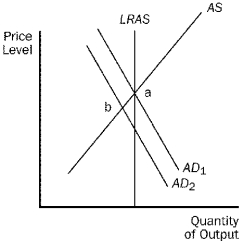 -Refer to Figure 21-7. Which of the following is correct?
-Refer to Figure 21-7. Which of the following is correct?
A) A wave of optimism could move the economy from point a to pointB
B) If aggregate demand moves from AD1 to AD2, the economy will stay at point b in both the short run and long run.
C) It is possible that either fiscal or monetary policy might have caused the shift from AD1 to AD2.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tax cut shifts the aggregate demand curve the farthest if
A) the MPC is large and if the tax cut is permanent.
B) the MPC is large and if the tax cut is temporary.
C) the MPC is small and if the tax cut is permanent.
D) the MPC is small and if the tax cut is temporary.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If it were not for the automatic stabilizers in the U.S. economy,
A) the Federal Reserve would have less reason than it has now to monitor stock prices.
B) it would be more desirable than it is now for the Federal Reserve to target an interest rate.
C) a strict balanced-budget rule would be more desirable than it is now.
D) output and employment would probably be more volatile than they are now.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The multiplier for changes in government spending is calculated as
A) 1/MPC.
B) 1/(1 - MPC) .
C) MPC/(1 - MPC) .
D) (1 - MPC) /MPC.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For the most part, fiscal policy affects the economy in the short run while monetary policy primarily matters in the long run.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The main criticism of those who doubt the ability of the government to respond in a useful way to the business cycle is that the theory by which money and government expenditures change output is flawed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In recent years, the Federal Reserve has conducted policy by setting a target for
A) bank reserves.
B) the monetary growth rate.
C) the exchange rate.
D) the federal funds rate.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following properly describes the interest-rate effect that helps explain the slope of the aggregate-demand curve?
A) As the money supply increases, the interest rate falls, so spending rises.
B) As the money supply increases, the interest rate rises, so spending falls.
C) As the price level increases, the interest rate falls, so spending rises.
D) As the price level increases, the interest rate rises, so spending falls.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both monetary policy and fiscal policy affect aggregate demand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A situation in which the Fed's target interest rate has fallen as far as it can fall is sometimes described as a
A) liquidity preference.
B) liquidity trap.
C) open-market trap.
D) interest-rate contraction.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following shifts aggregate demand to the right?
A) The price level rises.
B) The price level falls.
C) The money supply falls.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Other things equal, the higher the price level, the higher is the real wealth of households.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal policy refers to the idea that aggregate demand is affected by changes in
A) the money supply.
B) government spending and taxes.
C) trade policy.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government reduces taxes, which of the following decreases?
A) consumption
B) take-home pay
C) household saving
D) None of the above is correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fiscal stimulus was initiated by President Obama in response to the economic downturn of 2008-2009. At that time, the president's economists estimated the multiplier to be
A) 3.2 for government purchases and 2.0 for tax cuts.
B) 2.4 for government purchases and 1.4 for tax cuts.
C) 1.6 for government purchases and 1.0 for tax cuts.
D) 1.6 for government purchases and 0.4 for tax cuts.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 2009 President Obama and Congress increased government spending. Some economists thought this increase would have little effect on output. Which of the following would make the effect of an increase in government expenditures on aggregate demand smaller?
A) the MPC is small and changes in the interest rate have a small effect on investment
B) the MPC is small and changes in the interest rate have a large effect on investment
C) the MPC is large and changes in the interest rate have a small effect on investment
D) the MPC is large and changes in the interest rate have a large effect on investment
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 381 - 400 of 416
Related Exams