A) a decline in saving, but not a rise in investment
B) a rise in investment, but not a decline in saving
C) both a decline in saving and a rise in investment
D) neither a decline in saving nor a rise in investment
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 31-1
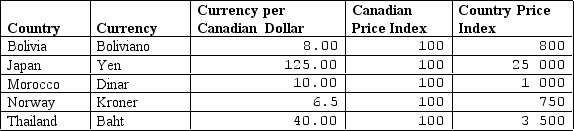 -Refer to Table 31-1. In real terms, Canadian goods are less expensive than goods in which of the following countries?
-Refer to Table 31-1. In real terms, Canadian goods are less expensive than goods in which of the following countries?
A) Bolivia and Morocco
B) Japan, Norway, and Thailand
C) Japan and Norway
D) Thailand
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a country exports $200 million of goods and services and imports $80 million of goods and services. What is the value of that country's net exports?
A) $280 million
B) $200 million
C) $120 million
D) -$200 million
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A British pharmacy buys drugs from a Canadian company and pays for them with British pounds. Which of the following correctly identifies the effects of this transaction?
A) It increases British net exports and increases Canadian capital outflow.
B) It increases British net exports and decreases Canadian capital outflow.
C) It decreases British net exports and increases Canadian capital outflow.
D) It decreases British net exports and decreases Canadian capital outflow.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
From 1970 to 1998, the Canadian dollar depreciated against the German mark and appreciated against the Italian lira because Canada experienced more inflation than Germany but less inflation than Italy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Many economists believe that the theory of purchasing-power parity describes the forces that determine exchange rates in the long run.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Net capital outflow is the purchase of domestic assets purchased by foreign residents minus the purchase of foreign assets by domestic residents.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best defines the nominal exchange rate?
A) It is the nominal interest rate in one country divided by the nominal interest rate in the other country.
B) It is the rate at which a person can trade the currency of one country for the currency of another.
C) It is the price of a good in one country divided by the price of the same good in another.
D) It is the number of goods a person can trade for a similar good in another country.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the formula for national saving?
A) S = I + C
B) S = I - NX
C) S = I + NCO
D) S = NX - NCO
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following was an important change in Canadian economy after 1999?
A) National saving fell below investment, and net capital outflow was a large positive number.
B) Net capital outflow turned positive.
C) Investment equalled saving every year.
D) Investment fell below saving, so net capital outflow was a large negative number.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Canadian computer maker sells computers to a German firm. This company uses all of the revenues from this sale to purchase automobiles from German firms. Which of the following best describes the effects of these transactions?
A) They will increase both Canadian net exports and Canadian net foreign investment.
B) They will decrease both Canadian net exports and Canadian net foreign investment.
C) They will increase Canadian net exports and will not affect Canadian net foreign investment.
D) They will not affect Canadian net exports or Canadian net foreign investment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Canada sells chocolate to the United States. Which of the following correctly identifies the effects of this transaction?
A) U.S. net exports increase, and U.S. net capital outflow increases.
B) U.S. net exports increase, and U.S. net capital outflow decreases.
C) U.S. net exports decrease, and U.S. net capital outflow increases.
D) U.S. net exports decrease, and U.S. net capital outflow decreases.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does purchasing-power parity explain?
A) It explains prices in the short run.
B) It explains prices in the long run.
C) It explains exchange rates in the short run.
D) It explains exchange rates in the long run.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ivan, a Russian citizen, sells several hundred cases of Russian caviar to a restaurant chain in Canada. Which of the following correctly identifies the effects of this transaction?
A) It increases Canadian net exports and has no effect on Russian net exports.
B) It increases Canadian net exports and decreases Russian net exports.
C) It decreases Canadian net exports and has no effect on Russian net exports.
D) It decreases Canadian net exports and increases Russian net exports.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do nominal exchange rates change over time?
A) They vary little over time.
B) They vary substantially over time.
C) They appreciate over time for most countries.
D) They depreciate over time for most countries.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For many questions in macroeconomics, international issues are peripheral.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does a trade deficit imply?
A) saving is greater than domestic investment and Y > C + I + G
B) saving is greater than domestic investment and Y < C + I + G
C) saving is less than domestic investment and Y > C + I + G
D) saving is less than domestic investment and Y < C + I + G
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to purchasing-power parity, if prices in Canada increase by a smaller percentage than prices in Algeria, how does the exchange rate change?
A) The real exchange rate, defined as Algerian goods per unit of Canadian goods, rises.
B) The real exchange rate, defined as Algerian goods per unit of Canadian goods, falls.
C) The nominal exchange rate, defined as Algerian currency per dollar, rises.
D) The nominal exchange rate, defined as Algerian currency per dollar, falls.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose inflation is higher in Canada over the next few months than in foreign countries, and exchange rates are given in terms of how much foreign currency a dollar buys or how many foreign goods Canadian goods buy. According to purchasing-power parity, which of the following should we expect to see?
A) Only the nominal exchange rate depreciates.
B) Both the real and nominal exchange rates appreciate.
C) Both the real and nominal exchange rates depreciate.
D) Only the real exchange rate appreciates.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an identity that always holds in an open economy?
A) NCO + C = NX
B) NCO = NX
C) NX - NCO = C
D) NX + NCO = C
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 215
Related Exams