A) slope of the budget constraint.
B) slope of an indifference curve.
C) marginal rate of substitution.
D) income effect.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Utility measures the
A) income a consumer receives from consuming a bundle of goods.
B) satisfaction a consumer receives from consuming a bundle of goods.
C) satisfaction a consumer places on her budget constraint.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are properties of indifference curves except
A) higher indifference curves are preferred to lower ones.
B) indifference curves are downward sloping.
C) indifference curves do not cross.
D) indifference curves are bowed outward.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jonathan is planning ahead for retirement and must decide how much to spend and how much to save while he's working in order to have money to spend when he retires.When the income effect dominates the substitution effect,an increase in the interest rate on savings will cause him to
A) decrease his savings rate.
B) increase his savings rate.
C) continue saving at the current rate.
D) Any of the above could be correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-2 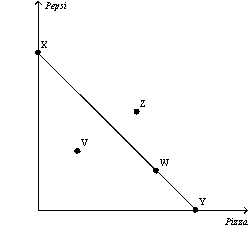 -Refer to Figure 21-2.A consumer that chooses to spend all of her income could be at which point(s) on the budget constraint?
-Refer to Figure 21-2.A consumer that chooses to spend all of her income could be at which point(s) on the budget constraint?
A) V only
B) Z only
C) V,W,X,or Y only
D) W,X,or Y only
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a consumer purchases more of good A when her income falls,good A is an inferior good.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-2  -Refer to Figure 21-2.Which points are affordable?
-Refer to Figure 21-2.Which points are affordable?
A) W,X,and Y only
B) Z only
C) V,W,X,and Y only
D) V,W,X,Y,and Z
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 21-1 Suppose the price of hot wings is $10,the price of beer is $1,and the consumer's income is $50.In addition,suppose the consumer's budget constraint illustrates hot wings on the horizontal axis and beer on the vertical axis. -Refer to Scenario 21-1.If the consumer's income rises to $60,then the budget line for hot wings and beer would
A) now intersect the horizontal axis at 6 orders of hot wings and the vertical axis at 60 beers.
B) not change.
C) now intersect the horizontal axis at 4 orders of hot wings and the vertical axis at 16 beers.
D) rotate outward along the beer axis.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the indifference curve map and budget constraint for two goods,X and Y.Suppose the good on the horizontal axis,X,is normal.When the price of X increases
A) the substitution effect and income effect both cause an increase in the consumption of X.
B) the substitution effect causes a decrease in the consumption of X,and the income effect causes an increase in the consumption of X.However,the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
C) the substitution effect causes an increase in the consumption of X,and the income effect causes a decrease in the consumption of X.However,the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
D) the substitution effect and income effect both cause a decrease in the consumption of X.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jake faces tradeoffs between consuming in the current period when he is young and consuming in a future period when he is old.Jake experiences a decrease in the current interest rate he earns on his savings.Jake will save
A) less in the current period if the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
B) less in the current period if the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
C) more in the current period if the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
D) more in the current period,regardless of the sizes of the income and substitution effects.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following diagram shows a budget constraint for a particular consumer. 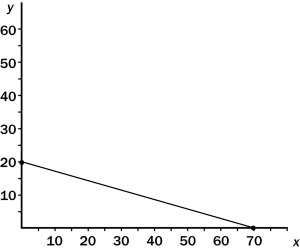 If the price of X is $10,what is the price of Y?
If the price of X is $10,what is the price of Y?
A) $15
B) $25
C) $35
D) $70
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that a college student purchases only coffee and Snickers bars.The substitution effect associated with a decrease in the price of a Snickers bar will result in
A) an increase in the consumption of coffee only.
B) a decrease in the consumption of coffee only.
C) an increase in the consumption of Snickers bars and a decrease in the consumption of coffee.
D) a decrease in the consumption of Snickers bars and an increase in the consumption of coffee.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that you have $100 today and expect to receive $100 one year from today.Your money market account pays an annual interest rate of 25%,and you may borrow money at that interest rate.If you save all your money,how much money will you have one year from today?
A) $100
B) $125
C) $200
D) $225
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The income effect of a price change is depicted by
A) a parallel shift of the budget constraint at the old set of prices.
B) a parallel shift of the budget constraint at the new set of prices.
C) a movement along the budget constraint holding the level of satisfaction constant.
D) not observable and is therefore neither a shift nor a change in the slope of the budget constraint.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-8 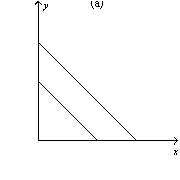
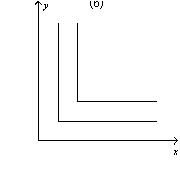
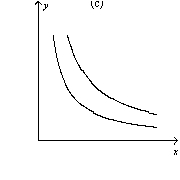 -Refer to Figure 21-8.Which of the graphs shown represent indifference curves for perfect complements?
-Refer to Figure 21-8.Which of the graphs shown represent indifference curves for perfect complements?
A) graph a
B) graph b
C) graph c
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The indifference curves for nickels and dimes are straight lines.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The consumer's optimum is where
A) MUx/MUy = Py/Px.
B) MUx/Py = MUy/Px.
C) Px/MUx = Py/MUy.
D) MUx/MUy = Px/Py.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-12 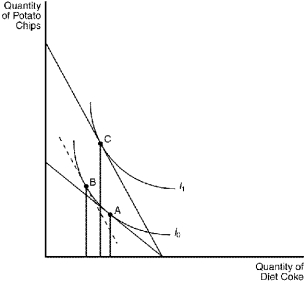 -Refer to Figure 21-12.If the consumer is currently at point A in the figure,a movement to point B as a result of a decrease in the price of potato chips represents the
-Refer to Figure 21-12.If the consumer is currently at point A in the figure,a movement to point B as a result of a decrease in the price of potato chips represents the
A) substitution effect.
B) income effect.
C) budget effect.
D) price effect.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As long as a consumer remains on the same indifference curve,
A) she is indifferent to all points that lie on any other indifference curve.
B) her preferences will not affect the marginal rate of substitution.
C) she is unable to decide which bundle of goods to choose.
D) she is indifferent among the points on that curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wilbur consumes two goods,bacon and eggs.He has maximized his utility given his income.Eggs costs $2 per dozen,and he consumes them to the point where the marginal utility he receives is 6.Bacon cost $4 per serving,and the relationship between the marginal utility that Wilbur gets from eating bacon and the number of servings he eats per month is as follows:
 How many servings of bacon does Wilbur buy each month?
How many servings of bacon does Wilbur buy each month?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 281 - 300 of 354
Related Exams