A) (i) and (ii) only
B) (ii) and (iii) only
C) (iii) only
D) (i) ,(ii) ,and (iii)
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 14-1 Consider a transportation corporation named C.R.Evans that has just completed the development of a new subway system in a medium-sized town in the Northwest.Currently,there are plenty of seats on the subway,and it is never crowded.Its capacity far exceeds the needs of the city.After just a few years of operation,the shareholders of C.R.Evans experienced incredible rates of return on their investment due to the profitability of the corporation. -Refer to Scenario 14-1.Which of the following statements is most likely to be true? (i) New entrants to the market know they will have a smaller market share than C.R.Evans currently has. (ii) C.R.Evans is most likely experiencing decreasing average total cost. (iii) C.R.Evans is a natural monopoly.
A) (i) and (ii) only
B) (ii) and (iii) only
C) (i) and (iii) only
D) (i) ,(ii) ,and (iii)
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Customers who purchase an audio CD from Sally's Sounds are charged 20% more than customers who purchase the audio CD from the Sally's Sounds website.This is an example of
A) perfect price discrimination.
B) price discrimination.
C) deadweight loss.
D) socially inefficient output.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 14-5
A monopolist faces the following demand curve:
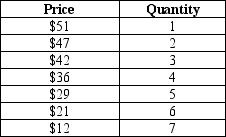 -Refer to Table 14-5.The monopolist has total fixed costs of $60 and has a constant marginal cost of $15.What is the profit-maximizing price?
-Refer to Table 14-5.The monopolist has total fixed costs of $60 and has a constant marginal cost of $15.What is the profit-maximizing price?
A) $4
B) $39
C) $36
D) $42
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The fundamental cause of monopolies is barriers to entry.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) The government may use antitrust laws to break up an existing company to improve competition.
B) The government may break up a natural monopoly to lower the price charged to customers.
C) Private ownership is typically preferred to public ownership.
D) Sometimes the best strategy is for the government to do nothing about monopoly inefficiency because the "fix" may be worse than the problem.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Two examples of early antitrust laws are the Clinton and Stigler Antitrust Acts.
B) Antitrust laws automatically prevent mergers between companies that produce similar products.
C) Antitrust laws reduce the government's power to regulate private companies.
D) Antitrust laws can reduce social welfare if they prevent mergers that would lower costs through more efficient joint production.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 14-3 A monopoly firm maximizes its profit by producing Q = 500 units of output.At that level of output,its marginal revenue is $30,its average revenue is $60,and its average total cost is $34. -Refer to Scenario 14-3.At Q = 500,the firm's marginal cost is
A) less than $30.
B) $30.
C) $34.
D) greater than $34.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A natural monopoly has economies of scale for most if not all of its range of output.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because a monopolist does not face competition from other firms,the outcome in a market with a monopoly
A) does not illustrate profit maximization.
B) is often not in the best interest of society.
C) is characterized by unlimited profits.
D) would be improved if the government produced the product rather than a private firm.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to sell more of its product,a monopolist must
A) sell to the government.
B) sell in international markets.
C) lower its price.
D) use its market power to force up the price of complementary products.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The simplest way for a monopoly to arise is for a single firm to
A) decrease its price below its competitors' prices.
B) decrease production to increase demand for its product.
C) make pricing decisions jointly with other firms.
D) own a key resource.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a constant marginal cost of $10,produces an output level of 100 units,and charges a price of $50.The socially efficient level of output is 200 units.Assume that the demand curve and marginal revenue curve are the typical downward-sloping straight lines.The monopoly deadweight loss equals $2,000.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In order for a firm to maximize profits through price discrimination,the firm must have some market power and be able to prevent arbitrage.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopolist's marginal costs increase by $1 for all levels of output,then the monopoly price will
A) rise by $1.
B) rise by more than $1.
C) rise by less than $1.
D) not change,but profits will decrease.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 14-6
A monopolist faces the following demand curve:
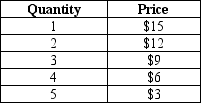 -Refer to Table 14-6.What is the marginal revenue from the sale of the 3rd unit?
-Refer to Table 14-6.What is the marginal revenue from the sale of the 3rd unit?
A) $-3
B) $3
C) $9
D) $24
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 14-8 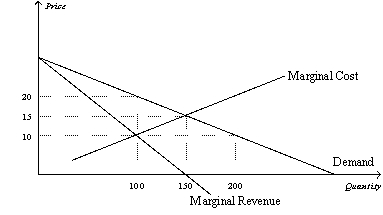 -Refer to Figure 14-8.To maximize its profit,a monopolist would choose which of the following outcomes?
-Refer to Figure 14-8.To maximize its profit,a monopolist would choose which of the following outcomes?
A) 100 units of output and a price of $10 per unit
B) 100 units of output and a price of $20 per unit
C) 150 units of output and a price of $15 per unit
D) 200 units of output and a price of $20 per unit
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 14-5 An airline knows that there are two types of travelers: business travelers and vacationers.For a particular flight,there are 100 business travelers who will pay $600 for a ticket while there are 50 vacationers who will pay $300 for a ticket.There are 150 seats available on the plane.Suppose the cost to the airline of providing the flight is $20,000,which includes the cost of the pilots,flight attendants,fuel,etc. -Refer to Scenario 14-5.How much profit will the airline earn if it engages in price discrimination?
A) -$5,000
B) $40,000
C) $55,000
D) $75,000
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Angelo is a wholesale meatball distributor.He sells his meatballs to all the finest Italian restaurants in town.Nobody can make meatballs like Angelo.As a result,his is the only business in town that sells meatballs to restaurants.Assuming that Angelo is maximizing his profit,which of the following statements is true?
A) Meatball prices will be less than marginal cost.
B) Meatball prices will equal marginal cost.
C) Meatball prices will exceed marginal cost.
D) Costs are irrelevant to Angelo because he is a monopolist.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist's profits with price discrimination will be
A) lower than if the firm charged a single,profit-maximizing price
B) the same as if the firm charged a single,profit-maximizing price.
C) higher than if the firm charged just one price because the firm will capture more consumer surplus.
D) higher than if the firm charged a single price because the costs of selling the good will be lower.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 526
Related Exams