A) an appreciation of the dollar,an increase in U.S.net exports,and so an increase in the quantity of dollars demanded in the foreign exchange market.
B) an appreciation of the dollar,a decrease in U.S.net exports,and so a decrease in the quantity of dollars demanded in the foreign exchange market.
C) a depreciation of the dollar,an increase in U.S.net exports,and so an increase in the quantity of dollars demanded in the foreign exchange market.
D) a depreciation of the dollar,a decrease in U.S.net exports,and so a decrease in the quantity of dollars demanded in the foreign exchange market.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the supply of loanable funds shifts right,then
A) the real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds both fall.
B) the real interest rate falls and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds rises.
C) the real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds both rise.
D) the real interest rate rises and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds falls.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an open economy,
A) net capital outflow = imports.
B) net capital outflow = net exports.
C) net capital outflow = exports.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the most likely response to an increase in the U.S.real interest rate?
A) a London bank purchases a U.S.bond instead of a Japanese bond it had considered purchasing
B) U.S.firms decide to buy more capital goods
C) a U.S.citizen decides to put less money in his savings account than he had planned.
D) All of the above are consistent.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same,an increase in the U.S.interest rate
A) raises net capital outflow which decreases the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
B) raises net capital outflow which increases the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
C) lowers net capital outflow which decreases the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
D) lowers net capital outflow which increases the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts right,then the exchange rate
A) rises and the quantity of dollars exchanged rises.
B) rises and the quantity of dollars exchanged does not change.
C) falls and the quantity of dollars exchanged falls.
D) falls and the quantity of dollars exchanged does not change.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same,if the real interest rate in a country falls,domestic residents will desire to purchase
A) more capital goods and more foreign bonds.
B) more capital goods but fewer foreign bonds.
C) more foreign bonds but fewer capital goods.
D) fewer capital goods and fewer foreign bonds.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the real exchange rate for the dollar appreciates,U.S.goods become
A) less expensive relative to foreign goods,which makes exports rise and imports fall.
B) less expensive relative to foreign goods,which makes exports fall and imports rise.
C) more expensive relative to foreign goods,which makes exports rise and imports fall.
D) more expensive relative to foreign goods,which makes exports fall and imports rise.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same,a decrease in the real interest rate raises the quantity of
A) domestic investment and net capital outflow.
B) domestic investment but not net capital outflow.
C) net capital outflow but not domestic investment.
D) neither domestic investment nor net capital outflow.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 32-2 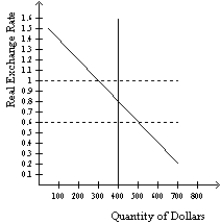 -Refer to Figure 32-2.If the real exchange rate is 1,then there is a
-Refer to Figure 32-2.If the real exchange rate is 1,then there is a
A) surplus of 100 so the real exchange rate will fall.
B) surplus of 100 so the real exchange rate will rise.
C) shortage of 100 so the real exchange rate will fall.
D) shortage of 100 so the real exchange rate will rise.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If at a given real interest rate desired national saving is $200 billion,domestic investment is $100 billion,and net capital outflow is $80 billion,then at that real interest rate in the loanable funds market there is a
A) surplus.The real interest rate will rise.
B) surplus.The real interest rate will fall.
C) shortage.The real interest rate will rise.
D) shortage.The real interest rate will fall.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an open economy,the source of the demand for loanable funds is
A) national saving
B) national saving + net capital outflow
C) investment + the government budget deficit
D) investment + net capital outflow
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is a surplus in the market for loanable funds,the resulting change in the real interest rate
A) reduces both the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
B) reduces the quantity of loanable funds supplied and raises the quantity of loanable funds demanded
C) raises both the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
D) raises the quantity of loanable funds supplied and reduces the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is considered part of the supply of U.S.dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange in the open-economy macroeconomic model?
A) both a U.S.bank wanting to lend money to a Canadian company and a U.S.firm wanting to buy computers made in South Korea
B) a U.S.bank wanting to lend money to a Canadian company,but not a U.S.firm wanting to buy computers made in South Korea
C) a U.S.firm wanting to buy computers made in South Korea,but not a U.S.bank wanting to lend money to a Canadian company
D) neither a U.S.bank wanting to lend money to a Canadian company nor a U.S.firm wanting to buy computers made in South Korea
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 32-1 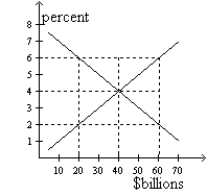 -Refer to Figure 32-1.If the real interest rate is 6 percent,the quantity of loanable funds demanded is
-Refer to Figure 32-1.If the real interest rate is 6 percent,the quantity of loanable funds demanded is
A) $20 billion,and the quantity supplied is $40 billion.
B) $20 billion,and the quantity supplied is $60 billion.
C) $60 billion,and the quantity supplied is $20 billion.
D) $60 billion,and the quantity supplied is $40 billion.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,the
A) exchange rate adjusts to equate private saving with the sum of investment,net exports,and net capital outflow.
B) exchange rate adjusts to equate national saving with the sum of investment and net capital outflow.
C) interest rate adjusts to equate private saving with the sum of investment,net exports,and net capital outflow.
D) interest rate adjusts to equate national saving with the sum of investment and net capital outflow.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A country has domestic investment of $200 billion.Its citizens purchase $600 of foreign assets and foreign citizens purchase $300 of its assets.What is national saving?
A) $400 billion
B) $500 billion
C) $600 billion
D) $800 billion
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of net exports equals the value of
A) national saving.
B) public saving.
C) national saving - net capital outflow.
D) national saving - domestic investment.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would make the equilibrium real interest rate decrease and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds increase?
A) The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
B) The demand for loanable funds shifts left
C) The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
D) The supply of loanable funds shifts left.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 32-2  -Refer to Figure 32-2.At what real exchange rate is the quantity of dollars demanded equal to 500?
-Refer to Figure 32-2.At what real exchange rate is the quantity of dollars demanded equal to 500?
A) 1
B) .8
C) .6
D) None of the above are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 141
Related Exams