A) increased and the labor-force participation rate of men has increased.
B) increased and the labor-force participation rate of men has decreased.
C) decreased and the labor-force participation rate of men has increased.
D) decreased and the labor-force participation rate of men has decreased.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wages in excess of their equilibrium level help explain
A) structural unemployment but not the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment but not structural unemployment.
C) both structural unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
D) neither structural unemployment nor the natural rate of unemployment.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that telemarketers are not unionized. If they unionize, then the supply of labor in other sectors of the economy will
A) decrease, raising wages in industries that are not unionized.
B) decrease, reducing wages in industries that are not unionized.
C) increase, raising wages in industries that are not unionized.
D) increase, reducing wages in industries that are not unionized.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 10-2
2009 Labor Data for Baltivia
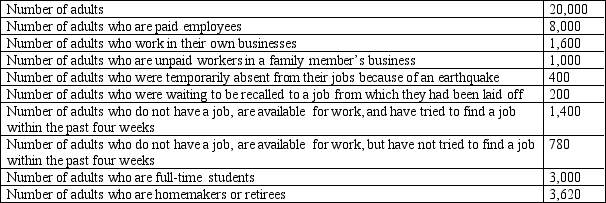 -Refer to Table 10-2. What was Baltivia's unemployment rate in 2009?
-Refer to Table 10-2. What was Baltivia's unemployment rate in 2009?
A) 8.0 percent
B) 12.7 percent
C) 15.9 percent
D) 22.1 percent
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spells of unemployment end about
A) 1/5 of the time with the person leaving the labor force.
B) 1/4 of the time with the person leaving the labor force.
C) 1/3 of the time with the person leaving the labor force.
D) 1/2 of the time with the person leaving the labor force.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics' U-5 measure of joblessness includes marginally attached workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a minimum-wage law forces the wage to remain above the level that balances supply and demand, the result is a shortage of labor.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Some long-run unemployment may be explained by the fact that the number of jobs available in some labor markets may be insufficient to give a job to everyone who wants one.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Figure 10-1. If unemployment is 2000 workers, then the minimum wage must be
A) $4.
B) $5.
C) $7.
D) $8.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wages in excess of their equilibrium level help explain
A) frictional but not structural unemployment.
B) structural but not frictional unemployment.
C) both frictional and structural unemployment.
D) neither frictional nor structural unemployment.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The labor-force participation rate is computed as
A) (Employed Adult Population) 100.
B) (Employed Labor Force) 100.
C) (Labor Force Adult Population) 100.
D) (Adult Population Labor Force) 100.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Policies that reduce the time it takes unemployed workers to find new jobs
A) can reduce both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
B) can reduce frictional unemployment, but it cannot reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
C) cannot reduce frictional unemployment, but it can reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
D) cannot reduce either frictional unemployment or the natural rate of unemployment.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the minimum wage is currently above the equilibrium wage, then a decrease in the minimum wage
A) increases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
B) decreases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
C) increases the quantity of labor demanded but decreases the quantity of labor supplied.
D) decreases the quantity of labor demanded but increases the quantity of labor supplied.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The normal rate of unemployment around which the unemployment rate fluctuates is called cyclical unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics' U-2 measure of joblessness includes job losers and job leavers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Frictional unemployment results from
A) job searching. It is often thought to explain relatively short spells of unemployment.
B) job searching. It is often thought to explain relatively long spells of unemployment
C) a surplus in the some labor markets. It is often thought to explain relatively short spells of unemployment.
D) a surplus in some labor markets. It is often thought to explain relatively long spells of unemployment.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is best to view the official unemployment rate as a useful but imperfect measure of joblessness.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Studies have shown that the design of the unemployment insurance system reduces the job search effort of the unemployed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
More than one-third of the unemployed are recent entrants into the labor force.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A minimum wage that is below the equilibrium wage rate does not raise unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 441 - 460 of 562
Related Exams