A) 6.5 percent
B) 6.9 percent
C) 7.0 percent
D) 17.9 percent
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that some people are counted as unemployed when, to maintain unemployment compensation, they search for work only at places where they are unlikely to be hired. If these individuals were counted as out of the labor force instead of as unemployed, then
A) both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be higher.
B) both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be lower.
C) the unemployment rate would be lower and the labor-force participation rate would be higher.
D) the unemployment rate would be higher and the participation rate would be lower.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that neither textile workers nor shoemakers are unionized. If textile workers unionize, then the supply of shoemakers will
A) rise and their wages will rise.
B) rise and their wages will fall.
C) fall and their wages will fall.
D) fall and their wages will rise.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Unions are exempt from U.S. antitrust laws.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The deviation of unemployment from its natural rate is called cyclical unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a cause of frictional unemployment?
A) the destruction of manufacturing jobs
B) a worker leaving a job to find one with better benefits
C) minimum-wage laws
D) unemployment insurance
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 10-3
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
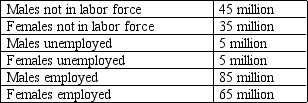 -Refer to Table 10-3. What is the adult population in Meditor?
-Refer to Table 10-3. What is the adult population in Meditor?
A) 90 million
B) 160 million
C) 230 million
D) 240 million
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One explanation for long-run unemployment is that it takes time for workers to search for the jobs that are best suited for them.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Table 10-5
2010 Labor Data for Tajnia
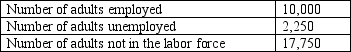 -Refer to Table 10-5. The labor force of Tajnia in 2010 is 10,000.
-Refer to Table 10-5. The labor force of Tajnia in 2010 is 10,000.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following causes of unemployment is not associated with a wage rate above the market equilibrium level?
A) efficiency wages
B) job search
C) minimum-wage laws
D) unions
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics counts a member of a surveyed household as an adult if that person is at least
A) 14 years old.
B) 16 years old.
C) 18 years old.
D) 21 years old.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Some of a firm's workers are made worse off by the introduction of a union.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An American worker who becomes unemployed typically receives 100% of her former salary during the first six months she is unemployed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions
A) and firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker effort both create frictional unemployment.
B) creates frictional unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker effort creates structural unemployment.
C) creates structural unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker effort creates frictional unemployment.
D) and firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker effort both create structural unemployment.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions contribute to
A) frictional unemployment but not the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment but not frictional unemployment.
C) both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
D) neither frictional unemployment nor the natural rate of unemployment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the U.S., the National Labor Relations Board is the government agency that enforces workers' right to unionize.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that the number of jobs for dental hygienists will grow faster than most occupations while the number of jobs for bookbinders will decline. This change in the labor market could lead to
A) frictional unemployment created by efficiency wages.
B) structural unemployment created by efficiency wages.
C) frictional unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
D) structural unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-1
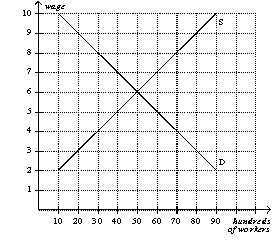 -Refer to Figure 10-1. If the government imposes a minimum wage of $4, then unemployment will increase by
-Refer to Figure 10-1. If the government imposes a minimum wage of $4, then unemployment will increase by
A) 0 workers.
B) 2000 workers.
C) 4000 workers.
D) 5000 workers.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) Nearly all economists believe that unions are bad for the economy as a whole.
B) Unionized firms pay wages above the competitive equilibrium level.
C) Unions increase the level of employment in unionized firms.
D) Unions decrease the level of employment in firms without unions.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The labor-force participation rate equals the percentage of the labor force that is employed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 562
Related Exams